Network Inference Challenge in silico Data
By Güngör Budak
- 2 minutes read - 303 wordsI had a meeting with BiGCaT this week and we discussed DREAM Breast Cancer Challenge. I presented the challenge and also some ways that I have found to solve the first sub-challenge network inference. Tina, from BiGCaT, suggested starting with in silico data which is much simpler than breast cancer data. Later, I can use the methods I develop for in silico data in experimental data.
in silico data contains 20 antibodies, 3 inhibitors and 2 ligand stimuli with 2 different concentration for each. And data for 10 time-points post-stimulus is provided. Inhibitors work by blocking the kinase domain of a protein. Any phosphorylated kinase is considered to be active and an inhibition on it also affects its downstream kinase activity. Inhibitors sequester away the unphosphorylated form of the target kinase and thus limit the amount of phosphorylated forms.
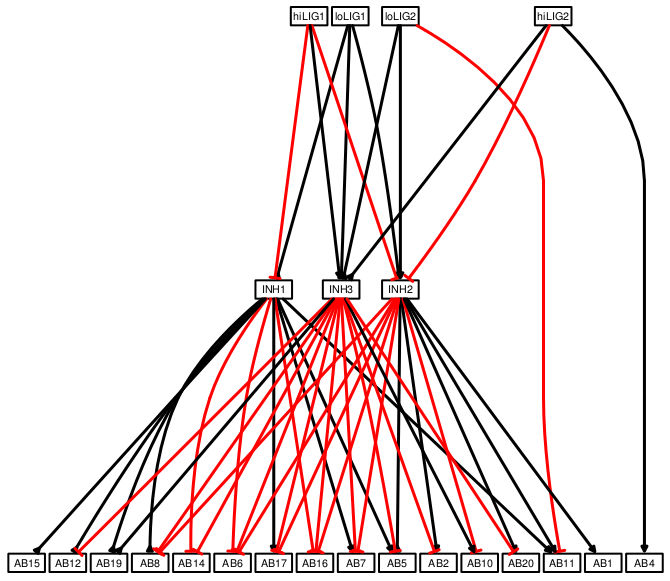
I used CellNOptR and CNORfeeder tools for network inference. CNORfeeder is a tool with several methods for network inference and it has its FEED method that creates boolean tables using the data and then it is possible to infer network based only on the data (i.e. data-derived network).
I plotted the network above using only expression data from the challenge in CNORfeeder. For this, mapBTables2model function that converts boolean table to network model should be called without a model or “model=NULL”. I had to convert treatment headers in MIDAS files into a different format because there is a small error in reading MIDAS and converting into CNOlist object: “TR:ABC:Stimuli” to “TR:ABC” and “TR:ABC:Inhibitors” to “TR:ABCi”. And a new form of makeBTables function CNORfeeder because there was no stimuli/no inhibitors condition in the data, which is not suitable for the old version.
CellNOptR and CNORfeeder have been developed by CNO developers from European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) more information can be found on their official website.