Mann Whitney U Test (Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test) Javascript Implementation
By Güngör Budak
- 2 minutes read - 404 wordsCurrently Javascript is really poor in statistical methods compared to Python (SciPy) and R. There are several efforts to fill this gap, most notably from jStat. However, still many functions, distributions and tests are missing in this library. In one of my projects, I had to implement a Javascript version of Mann Whitney U test (or also called Wilcoxon rank-sum test). Here, I’m giving a link to its source code and describing how it works.
Description
Mann Whitney U test is a nonparametric test with a null hypothesis that two samples belong to the same population. Consider you have two groups of numbers, they don’t follow any known distribution and you want to test if they are different. In such cases, you’d use Mann Whitney U test.
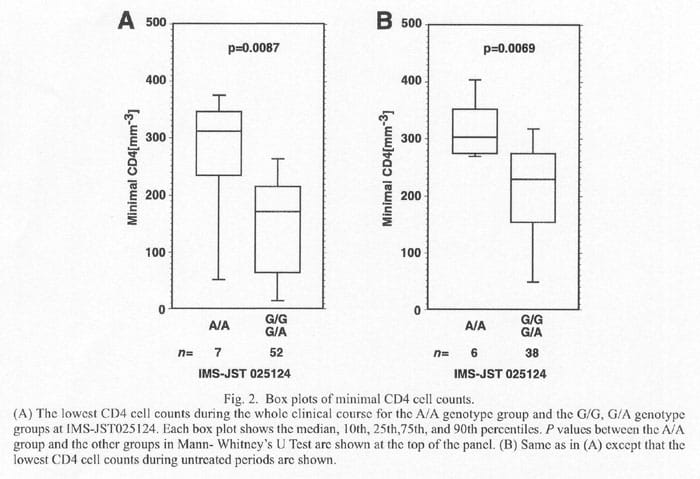
The above plots show that between two groups (A/A and G/G, G/A) minimal CD4 levels are significantly different (Kobayashi et al., Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 55, 131-133, 2002). And their significance are shown at the top as p-values.
This implementation is adapted from SciPy and R source codes and tested in both with several datasets.
GitHub Gist for Mann Whitney U test Javascript implementation (mannwhitneyu.js) .
How to use
Just download mannwhitneyu.js file and add a script tag to your HTML pointing the downloaded file and call the test with your datasets. Create a file called index.html and paste the following in it and save. Also make sure you place mannwhitneyu.js next to it.
1<html>
2<head>
3 <title>Mann Whitney U test</title>
4 <script type="text/javascript" src="mannwhitneyu.js"></script>
5</head>
6<body>
7 <script type="text/javascript">
8 var x = [2, 4, 6, 2, 3, 7, 5, 1],
9 y = [8, 10, 11, 14, 20, 18, 19, 9];
10 var t = mannwhitneyu.test(x, y, alternative = 'less');
11 console.log(t);
12 </script>
13</body>
14</html>
Open index.html, and look at Console (Ctrl + Shift + J), you’ll see the result;
Object {U: 0, p: 0.0004654861357875073}
This result shows that numbers in x are significantly different and smaller than the ones in y. The alternative argument can also be greater, which is again a one-sided test, testing if the first group has numbers that are significantly different and greater. Also, you may give two-sided as alternative, which will compute a two-sided test.
Soon, I’ll send this code to jStat and hopefully it’ll be available there. I’m also considering making it as a Node module so that developers can easily include it in their Node projects.